

Potassium nitrate and paclobutrazol increased fruit retention and average fruit weight in avocado.
Avocado, Avocado, Avocado, Avocado, Foliar application, Foliar Application, Fruit retention, fruit retention, KNO3, Paclobutrazol, PBZ, Potassium nitrate,
N Potassium nitrate and paclobutrazol increased fruit retention and weight in avocado .
The effect of foliar spraying of paclobutrazol (PBZ) + KNO3, and the addition of paclobutrazol (PZB) to the soil, during inflorescence development and flowering on vigorous new shoots, fruit set, fruit retention, fruit size and harvest yield in avocado cv Mendez was evaluated.
Ninety three-year-old cv Mendez avocado trees (on "Criollo" rootstock) of uniform size and approximately 2 m in height were selected from an irrigated commercial orchard in the Guadalajara region of Mexico in early September 2012.
In mid-September, when inflorescence development was occurring, 10 productive terminal branch inflorescences per tree were labeled.
Productive trees of avocado cv Mendez were sprayed with paclobutrazol (1 or 2%) or paclobutrazol (1 or 2%) + KNO3 (2%) during inflorescence development and flowering. In addition, soil applications of paclobutrazol (3 to 6 ml of Austar, applied around the trunk) were made. Austar is an Australian paclobutrazol formulation containing 250 g of active ingredient per liter. Foliar and soil applications were made on October 1, 2012, when trees were flowering and inflorescences were developing. Backpacks were used for spraying, and were applied at full coverage. There were 10 individual tree replications with 9 treatments (including the control) in a completely randomized block design.
Paclobutrazol (spray and/or soil application) + KNO3 spray treatmentswere found to be effective in reducing new shoot vigor, as determined by total shoot length at harvest on September 5, 2013 (Table 1). These treatments did not reduce the number of fruit present at January 5, 2013, or the number of fruit retained at harvest. Individual fruit weight increased by 46% (Table 1), which consequently increased fruit yield. The results indicate that the application of paclobutrazol at flowering is effective in increasing fruit size but not fruit retention.
Foliar application was apparently sufficient for this response, as no additional benefit was observed with the additional application of PBZ to the soil. The combination of PBZ with 2% KNO3 resulted in a 32% increase in the number of fruits retained until harvest when compared to PBZ alone. This contributed to the yield increase.
Table 1. Least squares mean of number of fruits present and total length of new shoots or January 5, 2013 and September 5, 2013.
Average individual and total fruit weight at harvest on September 5, for each of the comparisons of relevance.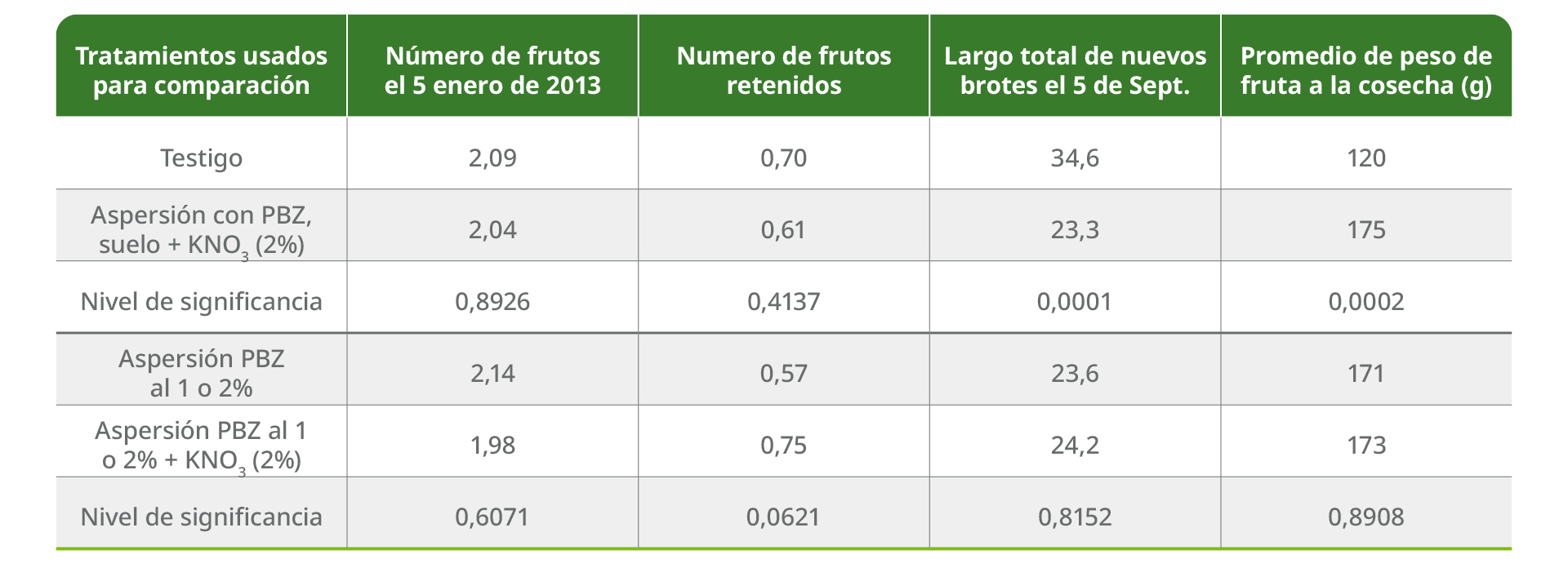
Autor
Oosthuyse, S.A. and M. Berrios. 2014. Effect of spray and/or soil application of paclobutrazol, and spray application of potassium nitrate during flowering on new shoot growth and cropping of 'Mendez' avocado. International Society for Horticultural Science (IHC Brisbane 2014): 1-6.


