

Benefits of potassium nitrate use for potato cultivation in Brazil
Brazil, Pivot irrigation, Soil application,
Demonstration trials in Brazil, which were repeated in 5 locations in 3 states for two years, showed a steady increase in yield (+ 8-15%), price per quality (+ 2-14%) and net income (+ 374-2223 USD/ha) in potato cultivation.
This was achieved by offering the grower a balanced nutrition program based on potassium nitrate, applied either as granular fertilizer (Nutrisystem®, the SQM VITAS brand of Qrop®), or wsNPK (Dripsol®, the SQM VITAS brand of Ultrasol®), by pivot irrigation.
This is an excellent example of the benefit of potassium nitrate by lateral application of granular cover crop and wsNPK, for field adjustment of the N : K ratio considering the requirement according to the phenological stage of the crop, increasing the percentage of nitrate nitrogen (N-NO3) in the total N applied, and reducing yield loss due to excessive chloride uptake by the plant.
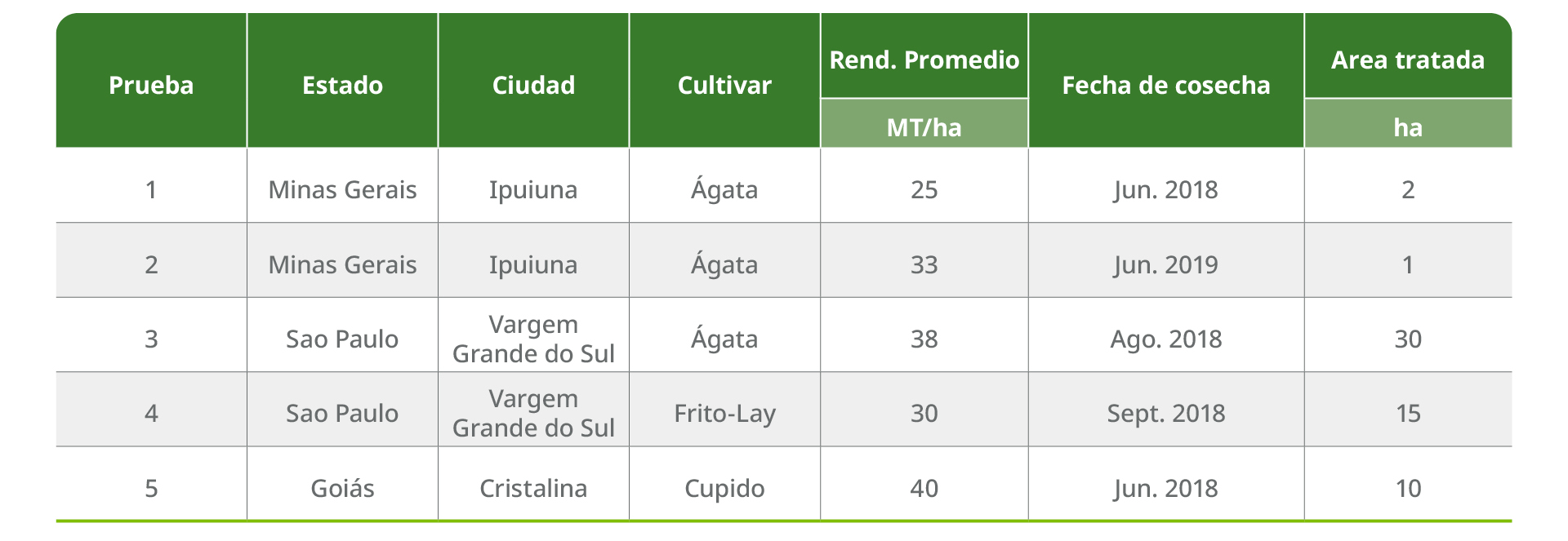
Table 1. Location and details of five assays conducted in 2018 and 2019 in Brazil by SQM VITAS.
Development of technical proposals focused on efficiency, profitability and sustainable production development. The custom-designed NPK formulas were included in a nutrition program that adjusts to the requirements of the phenological stage of the crop to increase yield, caliber and quality of the tubers, optimizing the efficiency of nutrient absorption by the plant.
The nutrition program was tailored to suit local growing conditions, farm economics and cropping systems.
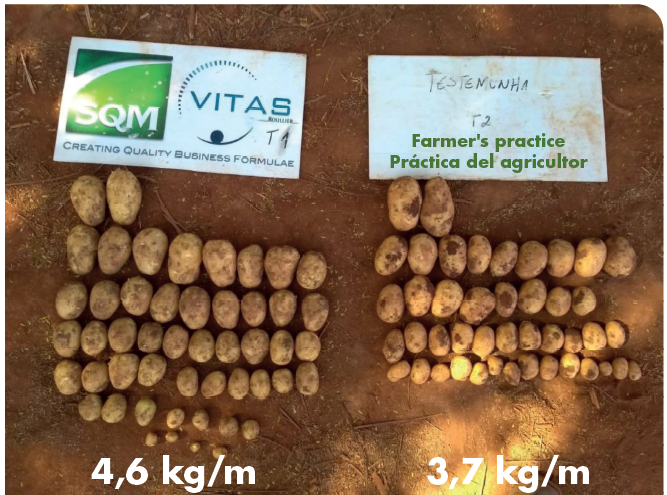

Figure 1. Total tuber weight of 1 linear meter (kg / m) per nutritional program. Agate cultivar, 70 days after planting (Test 3).
The overall objective of the project was to improve the current practice of farmers in the following aspects:
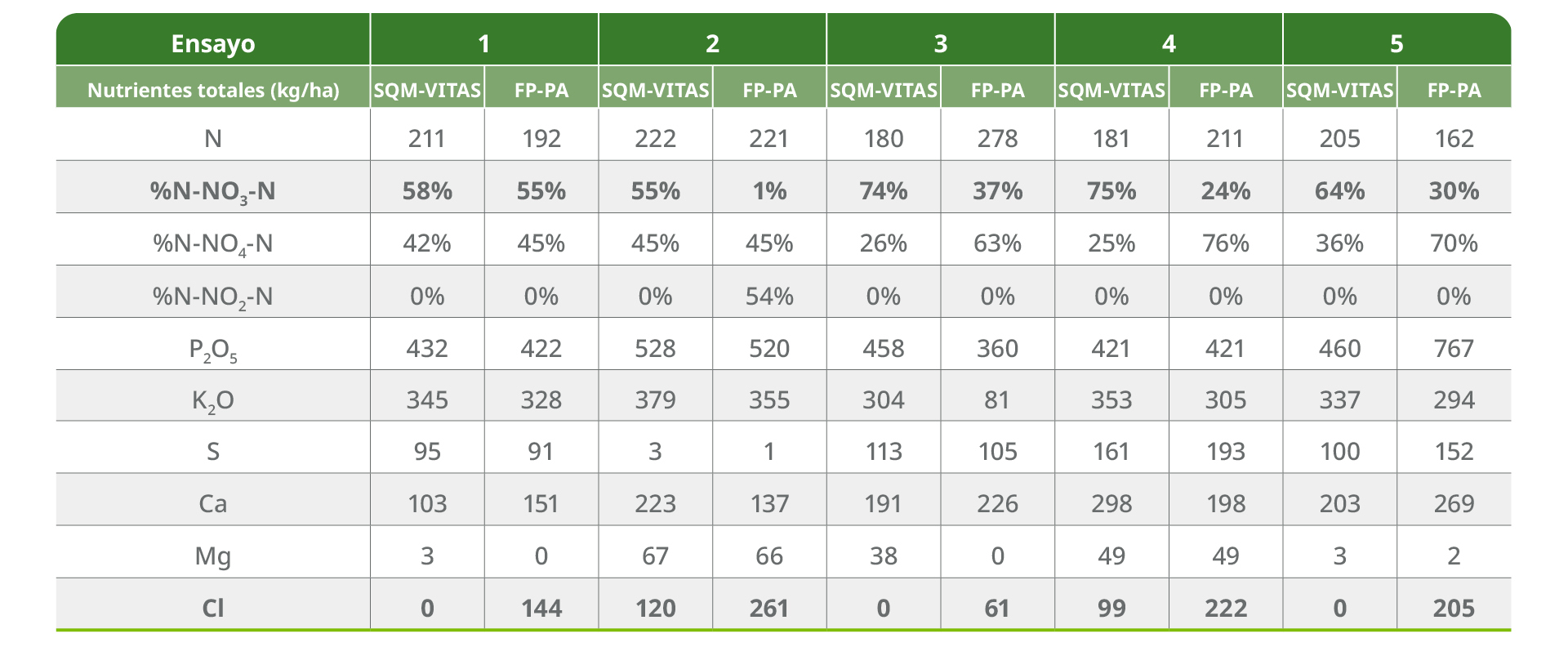
- Reduce chloride application by replacing KCl with KNO3, - Increase the proportion of N-NO3 in total N to reduce the risk of excessive chloride uptake and improve cation uptake. The inclusion of KNO3in the program allows the use of reduced amounts of low quality nitrogen sources that supply forms of nitrogen with high risk of loss to the environment after volatilization (N-NH2 and N-NH4), - Increase potassium availability during critical crop stages by adjusting the N: K ratio according to crop requirements by phenological stage.
Table 2. The SQM Vitas product line serves as a toolbox for designing balanced nutrient programs for potato growers.

The trials were conducted in farmers' fields (Table 1). A designated part of the area cultivated with the same potato cultivar under the same general crop management was fertilized with the SQM VITAS nutrition program and harvested separately from the area according to current farmers' practice (FP) (PA) to evaluate the difference in tuber yield and tuber distribution in different caliper classes. An economic analysis was conducted based on tuber productivity and quality using price differentiation. During the season, 1 linear meter samples were evaluated to record tuber number, size and weight as a standard part of the field trial protocol (Figures 1 and 2). This is routine for the SQM VITAS agronomist team. If the results are not in accordance with expectations, the nutrient program can be adapted to improve the final yield. For example, another time for the next application, a change in the N:K ratio or the balance of nitrogen sources can be suggested.
Table 3. Nutrients applied / ha in the 5 trials conducted in Brazil. PA = farmers' practice

Tuber size and linear meter yield in tuber filling of Frito-Lay cultivar in the SQM Vitas nutrient program ("SVB") and the farmer program ("Teste") (Trial 4).
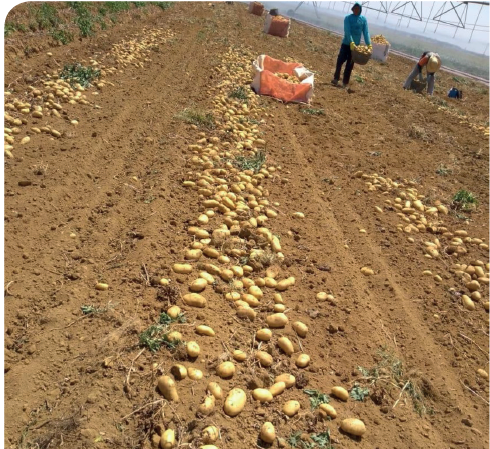

Figure 3. Harvest of Cupido cultivar, fertilized according to the SQM VITAS program, shows uniform tuber size (Test 5) (Test 5).
Potassium nitrate was applied by lateral or base dresssing as a cover or base fertilization, with a range of available granular fertilizers, the equivalent of SQM VITAS Brazil of the Qrop® brands: Nutrisystem® Inicial 42, Nutrisystem® Desenvolvimento or Nutrisystem® Produção. Additionally, water-soluble fertilizers were applied by pivot irrigation. These were the SQM VITAS Brazil equivalents of the Ultrasol® brands: Dripsol® Batata Produção, Dripsol® HF Produção (Table 2), Dripsol® NKS, Dripsol® MAP, Dripsol® SOP K +.
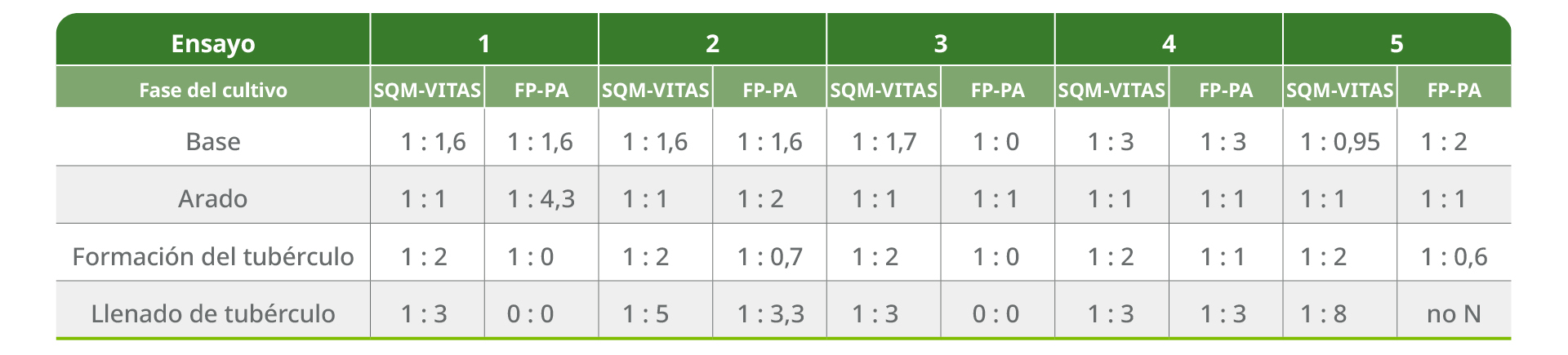
Table 4. Comparison of N:K2Oratio by crop stage between SQM Vitas nutritional program and farmers' practice (PA).
After harvest, the distribution of tubers in the different size classes was evaluated. The definition of quality classes in Brazil depends on tuber size and incidence of defects (disease or shape), but varies according to cultivar, harvest time and market. To facilitate comparison between trials, trials were reclassified for this publication according to the price range received for each quality class (Figure 5). The unit of yield in Brazil is the number of bags/ha, with 1 bag containing 50 kg.

Fifteen percent higher yield of well-developed tubers as a result of increasing the percentage of N-NO3 in the amount of total nitrogen, reduced phosphate in the base fertilizer and elimination of the chloride-containing fertilizer program (Exhibit 5).
Table 5. Tuber yield and farmer income analysis. 1 BEP = break-even point: the number of additional 50 kg bags/ha needed to return the investment in the SQM VITAS program, based on the same average price per bag. 2 net income = total income-fertilizer cost. Profit = (SQM net income - PA net income)/ PA net income; 3 yield units = 50 kg bags; 4 Assumed exchange rate at 1 USD = 3.7 BRL.
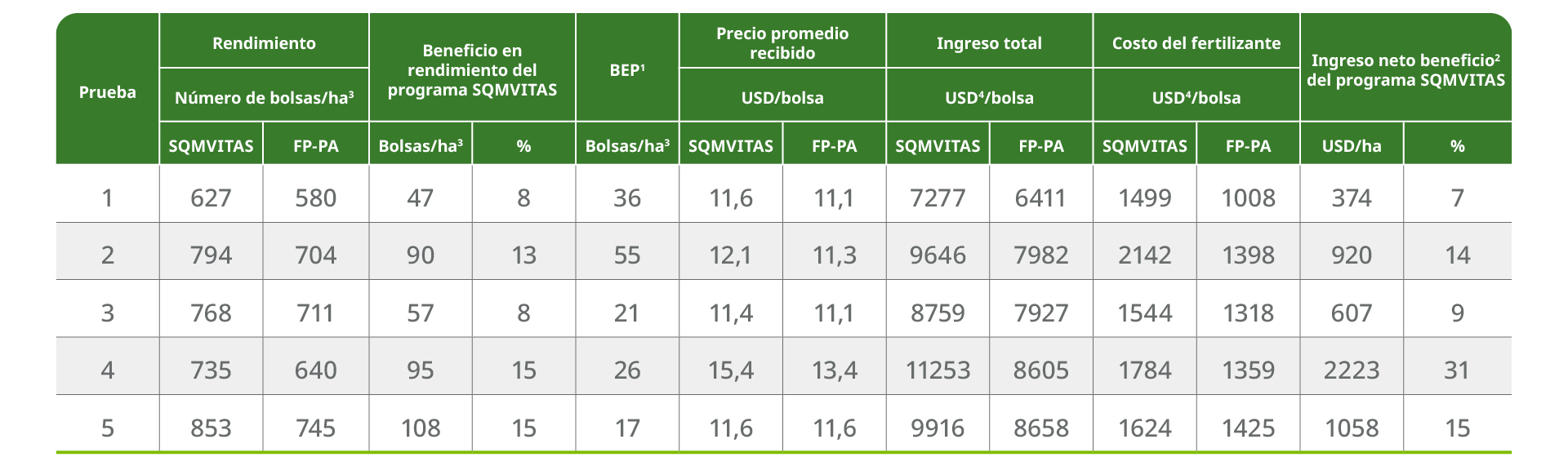
In any trial, this increase was more than enough to return the additional investment in the product, even if the price difference for quality was not considered in this calculation (Table 5).
STAGE OF CULTIVATION: I = Planting, II = Plowing, III = Tuber formation, IV = Tuber filling.
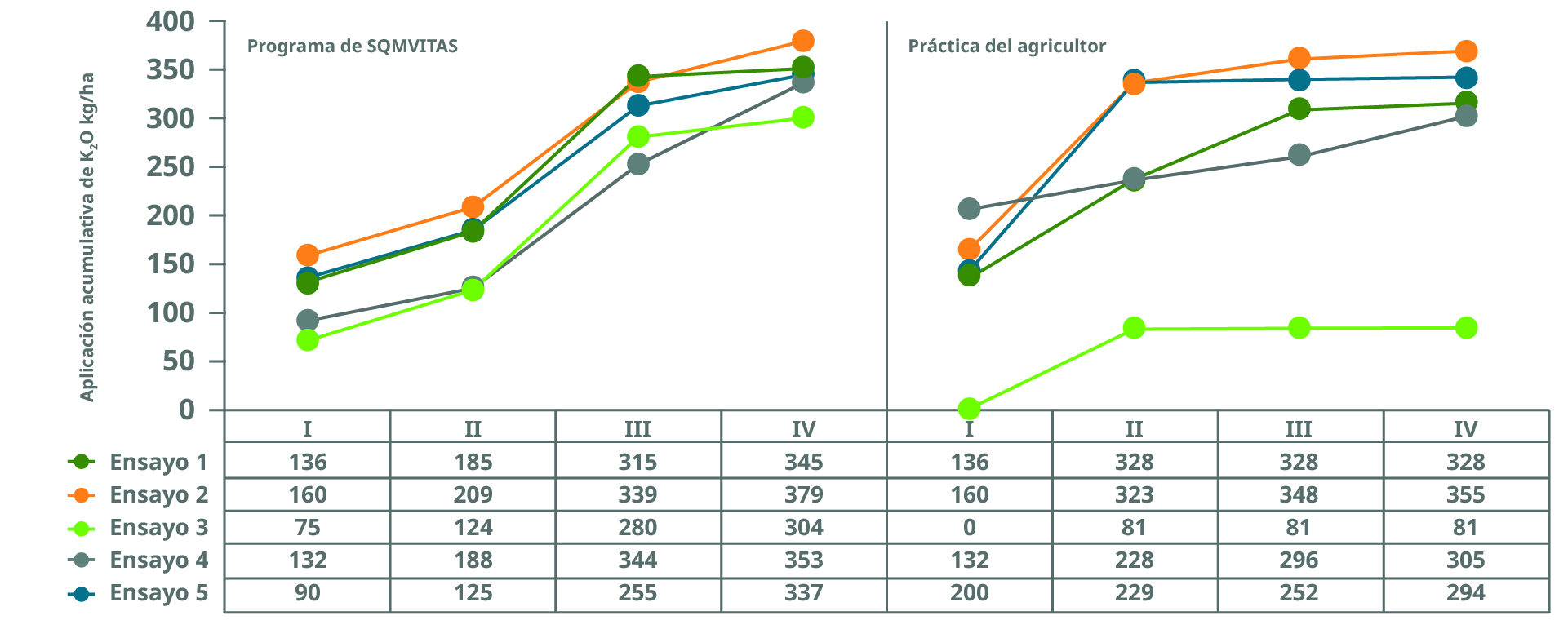 Potassium (K2O/ha) applied at each crop stage follows the crop requirement in the SQM Vitas program, in contrast to conventional farmer practice.
Potassium (K2O/ha) applied at each crop stage follows the crop requirement in the SQM Vitas program, in contrast to conventional farmer practice.
Outstanding results
The rational use of high quality fertilizers, proposed by SQM VITAS, together with the supply of corresponding NPK formulas and technical guidance for application was successful in supplying nutrients at the right time and in the exact amount required by the plants (Tables 3 and 4, Figure 5). Application of the SQM VITAS program resulted in higher yields in each of the 5 trials, increasing total yield by 8-15%: a difference of 47-108 bags, or 2.3-5.4 MT/ha compared to farmers' practice (Table 5).
The farmer's net income was further increased by an equally consistent increase in tuber size. For comparison across trials, size classes defined as "Extra", "Special", "Primera", "Pirulito", were grouped for each trial according to the price the grower received for the category at harvest (USD / 50 kg bag (Figure 6). When using the SQM VITAS program, 77-88% of the total yield received a higher price in trials 1-4, and this percentage was always higher compared to farmer practice. The average price received by the farmer, calculated from the total tuber yield in each size class, was higher for fields treated with SQM VITAS (Table 5). Averaged across all trials, 20% more premium-priced produce was harvested (+2.3 MT/ha).
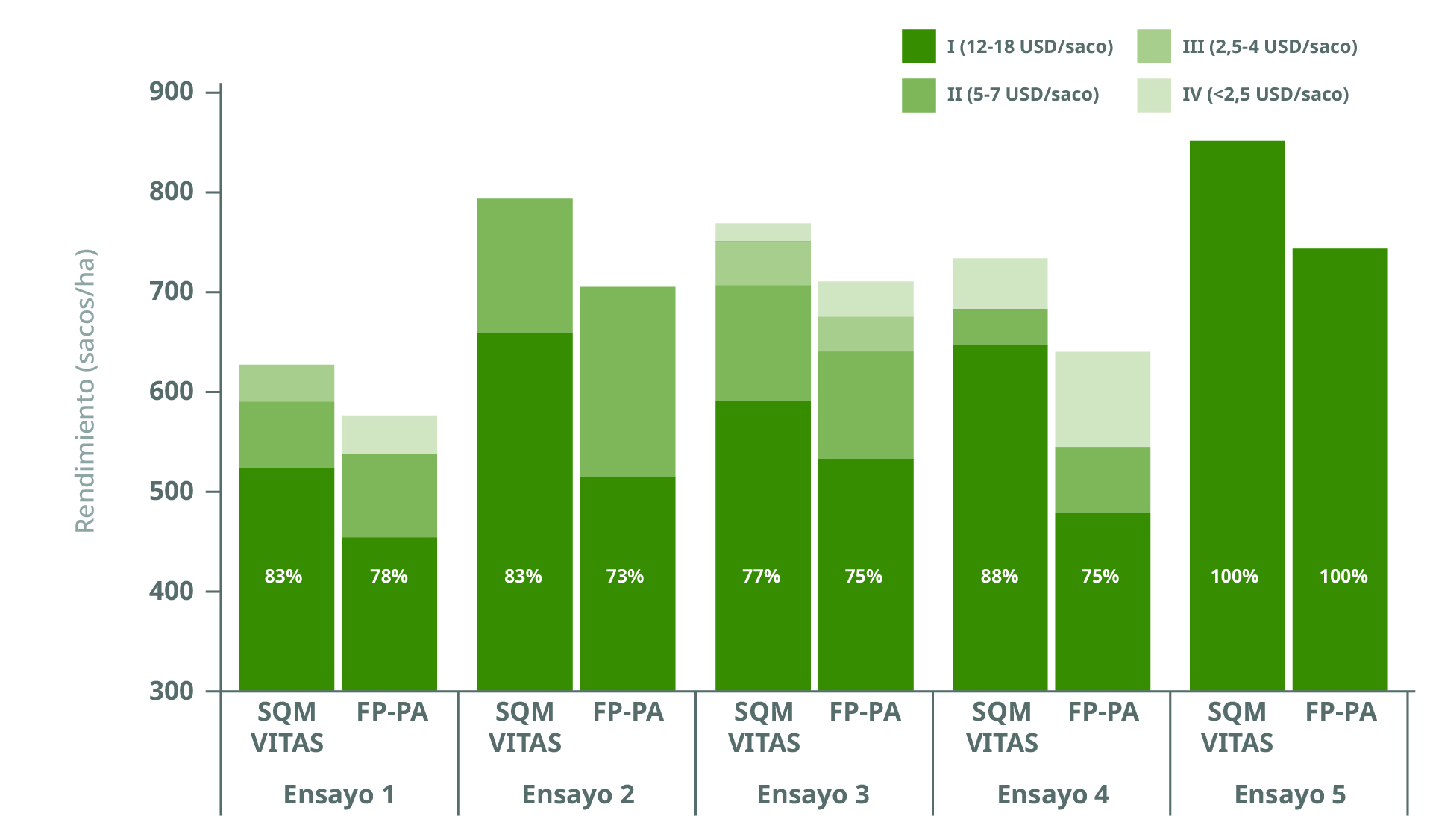 Figure 6. Distribution of quality classes on total potato yield after application of the SQM VITAS nutrient program, or farmers' practice (FP). Price category I: "Extra, Special" (12-18 USD/bag). Price category II: "Primeira, Segunda" (5-7 USD/bag), Price category III: "Diversas, Pirulito" (2.4-4 USD/bag),
Figure 6. Distribution of quality classes on total potato yield after application of the SQM VITAS nutrient program, or farmers' practice (FP). Price category I: "Extra, Special" (12-18 USD/bag). Price category II: "Primeira, Segunda" (5-7 USD/bag), Price category III: "Diversas, Pirulito" (2.4-4 USD/bag),
What's next?
With these results in hand, SQM VITAS' next steps will be to further develop the potassium nitrate market for potatoes:
- Implement nutrient application (dressing) in nutrition coverage by pivot irrigation to according to each phenological stage, - Expand the recommended nutritional program with the same farmers who conducted field trials during the 2018/2019 season, - Explore agronomic and economic results to serve as consistent arguments in presentations and seminars in order to reach other regions and potential farmers. - Increase the number of potassium nitrate applications during tuber filling to achieve higher yield (fresh market) and dry matter content (processing industry), - Promote additional phosphorus applications during vegetative growth by employing wsNPK instead of high doses of granular fertilizer in the base dressing,


